1. 서론
데이터베이스 시스템이나 어플리케이션 서버, 웹 서버를 운용하다 보면 어느순간 쌓여 있는 로그들을 확인할수 있다. 이렇게 쌓인 로그들은 운영중인 시스템에 장애가 발생했을때 원인을 찾기위해 자료로 활용되기 때문에, 로그를 확인하는 습관은 엔지니어가 가져야할 덕목이기도 하다.
하지만 사용자가 별다른 조치를 취하지 않는이상, 로그는 끊임없이 쌓이게 된다. 커머스 서비스라도 운영하게 된다면 GB 단위로 매일 로그가 쌓이게 될것이고, 스토리지의 용량이 꽉차게 된다면 장애가 발생하게 될것이다.
다행이 누군가 이러한 고민을 해결하기 위해 노력했고, 쌓인 로그들을 관리할수 있게 해주는 툴이 개발되었다. 그중 하나가 logrotate 유틸리티이다. 이번글에선 centos7 도커 컨테이너 환경에서의 logrotate 사용에 대해서 다루어보려 한다.
2. logrotate
logrotate는 리눅스 환경에서 로그의 관리를 도와주는 CUI 기반의 도구이다. logrotate는 사용자가 정한 주기 마다 쌓인 로그를 아카이브하고, 아카이브된 파일의 갯수가 사용자가 정한 최대 갯수보다 많아지면, 가장 오래된 순서로 아카이브된 로그 파일을 삭제한다.
이 과정을 통해 아카이브된 로그 파일들을 숫자나 타임스탬프로 구분할수 있어 향후 로그파일을 편리하게 확인할수 있고, 로그가 지나치게 쌓여서 스토리지의 용량이 부족해지는 문제를 방지할수 있다.
logrotate는 데몬이 아닌 실행파일이다. 항상 상주하는 프로세스가 아니기 때문에 주기적으로 작업할수 있는 능력이 없으므로 반드시 crond의 도움이 필요하다.
3. cron, nginx, logrotate 설치
가장먼저 cron, anacron, crontab, logrotate를 다음명령어로 설치해주자
yum install -y cronie logrotate
cronie 패키지는 anacron, crontabs 패키지를 기본적으로 같이 설치한다. 다음 명령어로 확인해볼수 있다.
rpm -q cronie rpm -q cronie-anacron rpm -q crontabs
설치가 완료되면 다음 명령어로 cron 데몬을 실행해준다.
crond # 도커 컨테이너가 아니라 쌩이면 다음 명령어로 crond를 실행한다. sudo systemctl start crond.service
yum install epel-release yum install nginx nginx
4. cron, anacron 동작구조
crond는 /etc/crontab 파일과 cron.d에 있는 crontab 파일들을 로드 하여 주기적인 작업을 실행한다. cron을 설치하면 자동으로 ‘cron.d/0hourly’ crontab 파일이 생성된다.
# Run the hourly jobs SHELL=/bin/bash PATH=/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin MAILTO=root 01 * * * * root run-parts /etc/cron.hourly
위 문장을 해석해보면 매시 1분 에 /etc/cron.hourly 폴더에 존재하는 스크립트들을 모두 실행한다는 의미이다. 그렇다면 /etc/cron.hourly 폴더에 있는 0anacron 스크립트 파일을 살펴보자
#!/bin/sh
# Check whether 0anacron was run today already
if test -r /var/spool/anacron/cron.daily; then
day=`cat /var/spool/anacron/cron.daily`
fi
if [ `date +%Y%m%d` = "$day" ]; then
exit 0;
fi
# Do not run jobs when on battery power
if test -x /usr/bin/on_ac_power; then
/usr/bin/on_ac_power >/dev/null 2>&1
if test $? -eq 1; then
exit 0
fi
fi
/usr/sbin/anacron -s
가장 맨 마지막 문장을 보면 anacron을 실행한다. 그렇다면 anacron은 어떤 기능을 제공하는 유틸리티 일까? anacron에 대해서 알아보기 위해 두가지 구조를 비교해보았다.
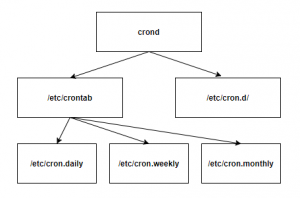
가장 일반적인 구조인 crond가 직접 crontab 파일들을 관리하는 형태를 가정해보았다. 만약 시스탬 장애 혹은 종료가 발생한다면 crond은 주기적으로 해야하는 작업을 실행하지 못한다. 향후 시스템이 복구가되도 crond 는 하지 못한 작업을 찾아서 실행하지 않는다.
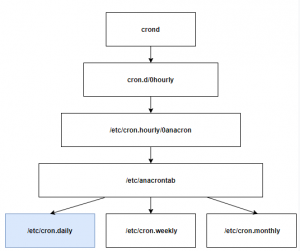
그러면 cron -> anacron -> crontab-files 구조로 주기적인 작업을 실행시키면 어떨까. 시스템 장애가 발생해서 복구되었든, 정상이든 anacron 유틸리티는 1시간마다 주기적으로 실행된다.
anacron 유틸리티는 /etc/anacrontab 파일을 로드하여 사용자가 정의한 작업들이 정해진 시간에 실행된적이 있는지를 점검한후, 수행한적이 없다면 다시 실행 시켜준다.그러면 /etc/anacrontab 파일을 살펴보자
# /etc/anacrontab: configuration file for anacron # See anacron(8) and anacrontab(5) for details. SHELL=/bin/sh PATH=/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin MAILTO=root # the maximal random delay added to the base delay of the jobs RANDOM_DELAY=45 # the jobs will be started during the following hours only START_HOURS_RANGE=3-22 #period in days delay in minutes job-identifier command 1 5 cron.daily nice run-parts /etc/cron.daily 7 25 cron.weekly nice run-parts /etc/cron.weekly @monthly 45 cron.monthly nice run-parts /etc/cron.monthly
맨 아래 문단의 첫번째 설정을 해석하면, 매일 /etc/cron.daily/ 폴더에 있는 스크립트들을 실행하라는 뜻이다. /etc/cron.daily/ 폴더를 확인해보면 우리가 그토록 원하던 logrotate 스크립트를 확인할수 있다.
5. logrotate 동작구조
/etc/cron.daily/logrotate 파일을 한번 확인해보자
#!/bin/sh /usr/sbin/logrotate -s /var/lib/logrotate/logrotate.status /etc/logrotate.conf EXITVALUE=$? if [ $EXITVALUE != 0 ]; then /usr/bin/logger -t logrotate "ALERT exited abnormally with [$EXITVALUE]" fi exit 0
첫번째 줄인 ‘/usr/sbin/logrotate -s /var/lib/logrotate/logrotate.status /etc/logrotate.conf’ 가 logrotate를 호출하는 명령문임을 알수 있다. ‘/etc/logrotate.conf’는 logrotate의 환경설정 파일이고 ‘/var/lib/logrotate/logrotate.status’는 logrotate가 실행된 기록임을 알수 있다. 그러면 /etc/logrotate.conf를 살펴보자
# see "man logrotate" for details
# rotate log files weekly
weekly
# keep 4 weeks worth of backlogs
rotate 4
# create new (empty) log files after rotating old ones
create
# use date as a suffix of the rotated file
dateext
# uncomment this if you want your log files compressed
#compress
# RPM packages drop log rotation information into this directory
include /etc/logrotate.d
# no packages own wtmp and btmp -- we'll rotate them here
/var/log/wtmp {
monthly
create 0664 root utmp
minsize 1M
rotate 1
}
/var/log/btmp {
missingok
monthly
create 0600 root utmp
rotate 1
}
# system-specific logs may be also be configured here.
6번째 문단을 보면 logrotate 유틸리티는 /etc/logrotate.d 폴더에 있는 사용자가 정의한 파일들을 로드하여 로그를 관리하게 된다. 즉 우리는 이 폴더에다가 nginx 로그를 관리하기 위한 작업파일을 작성하면 된다.
5. logrotate 작업 파일 작성
확인해봤더니 /etc/logrotate.d를 보면 이미 nginx 로그를 관리하기 위한 작업파일이 있었다. 이를 그대로 활용해도 되지만 지우고 나만의 작업파일을 작성해보자. touch 명령어로 원하는 이름의 작업파일을 만들고 다음과 같이 작성했다.
/var/log/nginx/*.log {
create 0664 nginx root # 새로운 로그 파일이 생성될때 소유자, 소유그릅 지정
daily # 작업주기
rotate 10 # 최대 아카이브 파일갯수
dateext # 아카이브시 타임스탬프를 뒤에다 붙이는 옵션
missingok # 로그파일이 없으면 생성
notifempty
sharedscripts
postrotate # logrotate 작업이후에 실행될 명령문들
/bin/kill -USR1 `cat /run/nginx.pid 2>/dev/null` 2>/dev/null || true
endscript
}
더 logrotate에 대해 자세히 알고 싶다면 아래의 메뉴얼을 참고하자
https://linux.die.net/man/8/logrotate
nginx의 경우 access.log, error.log 두가지의 로그 파일이 있다. 와일드카드를 사용하여 ‘*.log’ 로 표현하면 두개의 로그에대해 같은 설정으로 관리할수 있다.
postrotate 는 왜 필요할까? 쌓였던 access.log와 error.log 아카이브하고 새로운 access.log와 error.log를 생성하는것까지는 좋은데 nginx가 로그를 아카이브된 파일에 계속 로그를 쌓으려는 현상이 발생한다.
따라서 nginx에 별도의 신호를 보내 새로운 파일에 로그를 쌓을수 있게 해줘야 한다. ‘/bin/kill -USR1 `cat /run/nginx.pid 2>/dev/null` 2>/dev/null || true’ 가 그역활을 해준다.
6. logrotate 작업 테스트
다음 명령어를 입력하여 우리가 작성했던 logrotate가 제대로 도는지 확인할수 있다.
logrotate -d /etc/logrotate.conf
다음과 같이 뜨면 우리가 작성한 작업파일에 문제가 없다는 의미이므로, logrotate가 주기적으로 로그를 관리하는 모습을 볼수 있을것이다.
rotating pattern: /var/log/nginx/*.log after 1 days (10 rotations) empty log files are not rotated, old logs are removed considering log /var/log/nginx/access.log log does not need rotating (log is empty) considering log /var/log/nginx/error.log log does not need rotating (log is empty) not running postrotate script, since no logs were rotated
만약 지금 급하게 로그를 로테이트 해야한다면 다음 명령어를 사용한다.
logrotate -f /etc/logrotate.conf
logrotate의 작업이 끝나면 기존에 로그가 쌓이고 있던 파일들은 따로 날짜가 붙어서 아카이브 되고, 새롭게 로그가 쌓일 파일들이 생성되었음을 다음과 같이 확인할수 있다.
[root@7055eaac9a32 nginx]# ls -al total 20 drwxrwx--- 2 nginx root 4096 Apr 22 06:30 . drwxr-xr-x 1 root root 4096 Apr 22 06:26 .. -rw-rw-r-- 1 nginx root 0 Apr 22 06:30 access.log -rw-rw-r-- 1 nginx root 90 Apr 22 06:29 access.log-20200422 -rw-rw-r-- 1 nginx root 0 Apr 22 06:30 error.log -rw-rw-r-- 1 nginx root 168 Apr 22 06:29 error.log-20200422
logrotate 기록이 쌓이는 /var/lib/logrotate/logrotate.status 파일도 확인해보면 access.log, error.log에 대한 관리 기록을 확인해볼수 있다. logrotate는 기록파일을 확인하여 로그들을 로테이트 할것인지 말것인지를 판단한다. logrotate 실행시 -s 옵션과 다른 파일경로를 주어서 다른 기록 파일을 사용할수 있다.
logrotate state -- version 2 "/var/log/nginx/error.log" 2020-4-22-6:30:39 "/var/log/nginx/access.log" 2020-4-22-6:30:39
7. 참고자료
https://linux.die.net/man/8/logrotate
https://webdir.tistory.com/175

좋은 내용 써주셔서 감사합니다.
한가지 더 추가하자면 로그로테이트를 처음 추가하게 되면 로그가 쌓여있더라도 쌓인지 24시간이 지나지 않은 파일인 경우에도 ‘log does not need rotating’ 이라는 구문이 에러에 추가가 되면서 로테이트 되지 않습니다.
24시간이 지나게 되면 즉 하루가 지나게 되면 정상적으로 로테이트가 되기 때문에 해당 내용 참고해 주시면 좋을 것 같습니다.
호호호 피드백 해주셔서 감사합니다. 곧 반영해보도록 하겠습니다